Listing network interfaces in tcpdump:
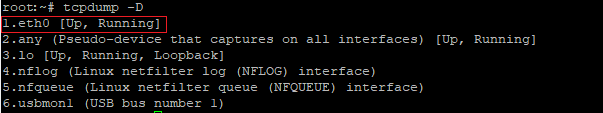
In order to show a list of network interfaces used in the system, you must specify the -D parameter
tcpdump -D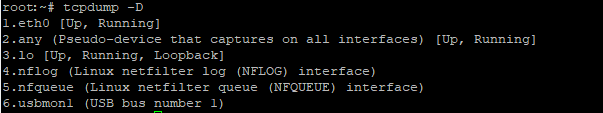
Capturing packets from a specific network interface
By default, Tcpdump listens on the lowest numbered network interface in the list.
to listen on a specific network interface, you must use the -i option with the interface name as a parameter
For example, listening to all local (Loopback) traffic
tcpdump -i loPacket capture from all available interfaces
If it is necessary to capture traffic from all network interfaces, for example, if there are several network connections in the system, tcpdump provides a special “name” any for such cases
tcpdump -i anyOutput of IP address, without conversion to DNS name
tcpdump -n17:19:39.440334 IP 192.168.3.7.22 > 192.168.3.10.51092: Flags [.], ack 720, win 36, length 0
Customize output verbosity tcpdump
tcpdump -v
tcpdump -vv
tcpdump -vvvvCapturing packets with a specific IP address or subnet tcpdump
Capturing packets from an IP address 8.8.8.8
tcpdump src 8.8.8.8Packet capture, sourced from subnet 192.168.0.0/24
tcpdump src net 192.168.0.0/24Packet capture with destination IP address 192.168.0.1
tcpdump dst 192.168.0.1
Capturing packets to the 192.168.10.0/24 subnet
tcpdump dst net 192.168.10.0/24Capturing packets between two hosts or two subnets tcpdump
Capturing packets from 10.0.0.1 to 192.168.0.1
tcpdump src 10.0.0.1 and dst 192.168.0.1Capturing packets from network 10.0.0.0/24 to subnet 192.168.0.0/24
tcpdump src net 10.0.0.0/24 and dst net 192.168.0.0/24Capturing packets between 10.0.0.1 and 192.168.0.1 in both directions
tcpdump host 10.1.0.52 and host 192.168.10.52
Packet capture between two subnets 10.0.0.0/24 and 192.168.0.0/24 in both directions
tcpdump net 10.0.0.0/24 and net 192.168.0.0/24Capturing packets from a specific network protocol
tcpdump allows you to capture network traffic of a specific network protocol. Known Layer 3 or Layer 4 protocols require their names to be specified.
Capture only IP packets
tcpdump ipCapture only ICMP packets
tcpdump icmpCapture only ARP packets
tcpdump arp
Capturing TCP packets
tcpdump tcpCapturing UDP packets
tcpdump udpCapture only TCP packets between 10.10.0.1 and 192.168.1.1 in both directions
tcpdump tcp and host 10.10.0.1 and host 192.168.1.1Capturing packets from specific TCP/UDP ports
Capturing packets with destination port 80
tcpdump dst port 80Capturing UDP packets from port 6000
tcpdump udp src port 6000Capture DNS packets (source or destination port 53)
tcpdump port 53Packet capture with 80 or 8080 ports
tcpdump port 80 or port 8080Capture packets in the range of ports from 1000 to 10000
tcpdump portrange 1000-10000Capturing packets other than a specific one
Exclude all SSH (port 22) packets with IP 192.168.0.100
tcpdump port not 22 and not host 192.168.0.100Capturing packets with a specific MAC address
Capturing broadcast traffic (packets with destination MAC address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff)
tcpdump ether dst ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ffPacket capture between 2f:c0:1b:21:4a:c4 and 7a:f4:2b:96:0b:41 in both directions
tcpdump ether host 2f:c0:1b:21:4a:c4 and ether host 7a:f4:2b:96:0b:41Capture packets sent or received 2f:c0:1b:21:4a:c4
tcpdump ether host 2f:c0:1b:21:4a:c4Saving captured packets to a file (pcap) tcpdump
Save first 1000 packets to save.pcap file:
tcpdump -c 1000 -w save.pcap
Reading a PCAP file
Reading TCP packets from a file
tcpdump -r save.pcap tcpRotate PCAP files every 30 minutes, with timestamps
tcpdump -w /tmp/save-%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M.pcap -G 1800Capture packets with high precision timestamps
tcpdump --time-stamp-precision nanoTimestamp in date, hour, minute, second, and microsecond format
tcpdump -ttttCapturing TCP SYN packets
tcpdump "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn) != 0"